Understanding the Mechanics of Modern Braking Systems
The ability to control a vehicle's speed and bring it to a safe halt is paramount for road safety, a function primarily managed by its braking system. Modern automotive braking systems are sophisticated assemblies of mechanical, hydraulic, and electronic components working in concert to convert kinetic energy into thermal energy through friction, thereby decelerating the vehicle. This intricate process is vital for the safety of drivers, passengers, and pedestrians, constantly evolving with advancements in engineering and technology to offer enhanced performance and reliability in diverse driving conditions.
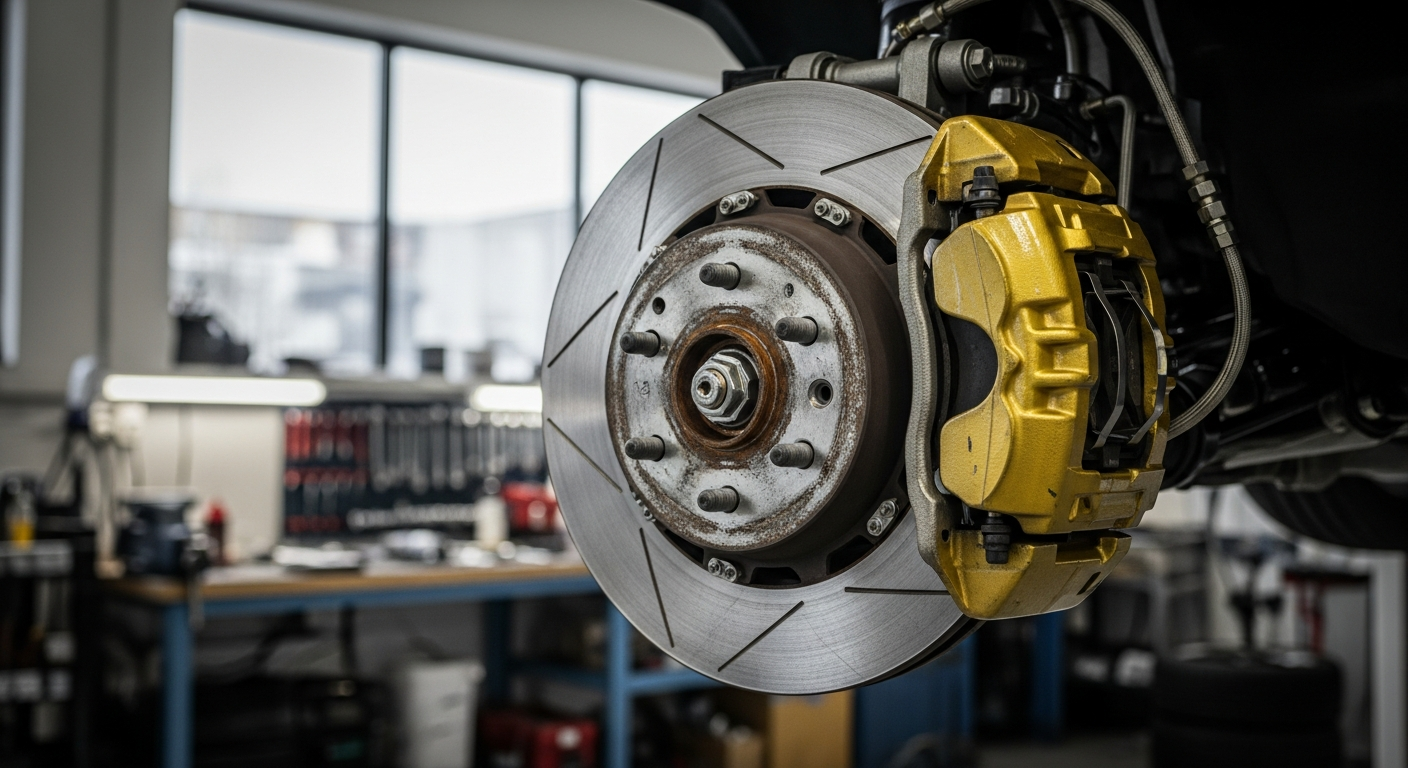
Evolution of Automotive Braking Technology
The journey of automotive braking technology reflects a continuous pursuit of greater safety and control. Early vehicles relied on simple mechanical linkages, often activating brake shoes directly against the wheels. The advent of hydraulic systems marked a significant leap, allowing for more uniform and powerful braking force distribution to all wheels with less effort from the driver. This innovation dramatically improved stopping distances and driver comfort. Further advancements introduced vacuum-assisted power brakes, reducing the physical effort required to apply the brakes, making driving more accessible and less fatiguing, especially in heavy transport applications. The consistent push for innovation has transformed these fundamental systems into the highly responsive and integrated components seen in contemporary vehicles.
Core Principles of Braking Mechanics
At its heart, a modern braking system operates on the principle of friction. When the driver presses the brake pedal, hydraulic fluid is pressurized and transmitted through lines to calipers at each wheel. These calipers then clamp brake pads against rotating discs (disc brakes) or push shoes against drums (drum brakes), creating friction that resists the wheel’s rotation. This resistance converts the vehicle’s kinetic energy into heat, slowing it down. The efficiency and performance of this process are critical for effective deceleration. Engineering principles are applied to material selection for pads and discs, ensuring optimal friction coefficients, heat dissipation capabilities, and resistance to wear, all contributing to reliable stopping power and overall vehicle mechanics.
Enhancing Driving Safety and Control
Beyond basic friction, modern braking systems incorporate advanced technologies to bolster driving safety and control. Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) prevent the wheels from locking up during hard braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control and potentially navigate around obstacles. Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD) automatically adjusts the braking force to each wheel based on road conditions and vehicle load, optimizing stopping performance. Traction Control Systems (TCS) and Electronic Stability Control (ESC) integrate with the braking system to prevent wheelspin and maintain vehicle stability during acceleration or cornering, significantly improving overall vehicle navigation and accident prevention. These systems collectively represent a major advancement in active safety features, crucial for contemporary mobility.
Design Considerations for Braking Efficiency
The design of braking components is a complex interplay of factors aimed at maximizing efficiency and durability. Engineers consider weight, material composition, and aerodynamic properties to minimize unsprung mass and improve handling. Ventilation designs for brake discs are crucial for dissipating heat rapidly, preventing brake fade and ensuring consistent performance even under strenuous conditions. The integration of regenerative braking in electric and hybrid vehicles represents a significant step towards sustainability and efficiency. This technology captures kinetic energy during deceleration and converts it back into electrical energy to recharge the battery, reducing wear on conventional brake components and enhancing overall propulsion system efficiency. Careful design ensures that the braking system not only performs its primary function but also contributes to the vehicle’s overall performance and longevity.
Future Trends in Braking Systems
The landscape of braking systems continues to evolve with emerging technologies. “Brake-by-wire” systems, which replace traditional hydraulic connections with electronic signals, offer faster response times, greater flexibility in system design, and the potential for advanced integration with autonomous driving features. These systems promise enhanced precision and adaptability to varying driving scenarios. Developments in material science are leading to lighter, more durable, and more heat-resistant components, further improving performance and sustainability. As vehicles become more connected and autonomous, braking systems will play an even more critical role, requiring sophisticated sensors and artificial intelligence to make instantaneous, precise decisions, propelling automotive technology towards new frontiers of safety and efficiency in transport.
Conclusion
Modern braking systems are a cornerstone of vehicle safety and performance, embodying decades of engineering excellence and technological innovation. From the foundational principles of friction to advanced electronic aids and future-forward brake-by-wire concepts, each development aims to provide drivers with greater control, shorter stopping distances, and enhanced overall driving confidence. As the automotive industry continues its trajectory towards increasingly intelligent and sustainable mobility solutions, the evolution of braking systems will remain a key area of focus, ensuring that vehicles can not only move efficiently but also stop reliably.






